Important Safety Information
Indications And Usage
CAROSPIR is an antagonist of aldosterone indicated for:
- the treatment of NYHA Class III-IV heart failure and reduced ejection fraction to increase survival, manage edema, and to reduce the need for hospitalization for heart failure
- use as an add-on therapy for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure in adult patients. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions
- the management of edema in adult cirrhotic patients when edema is not responsive to fluid and sodium restrictions
Contraindications
CAROSPIR is contraindicated for patients with the following conditions:
- Hyperkalemia
- Addison’s disease
- Concomitant use of eplerenone
Warnings And Precautions/Adverse Reactions
CAROSPIR may cause the following conditions.
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypotension and Worsening Renal Function
- Electrolyte and Metabolic Abnormalities
- Gynecomastia
- Impaired neurological function/ coma in patients with hepatic impairment, cirrhosis and ascites
The most common adverse reaction (incidence > 5%) with CAROSPIR treatment is the increased occurrence of gynecomastia in men.
Talk to your healthcare provider about other possible side effects with CAROSPIR. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact CMP Pharma, INC. at 1-844-321-1443 , or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/MedWatch.
Administration
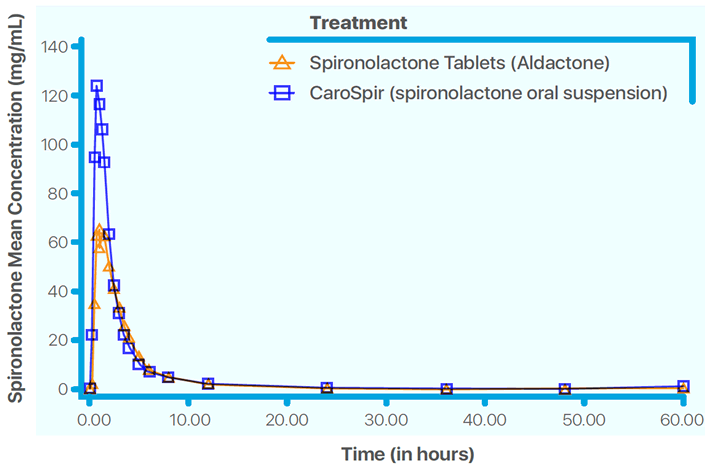
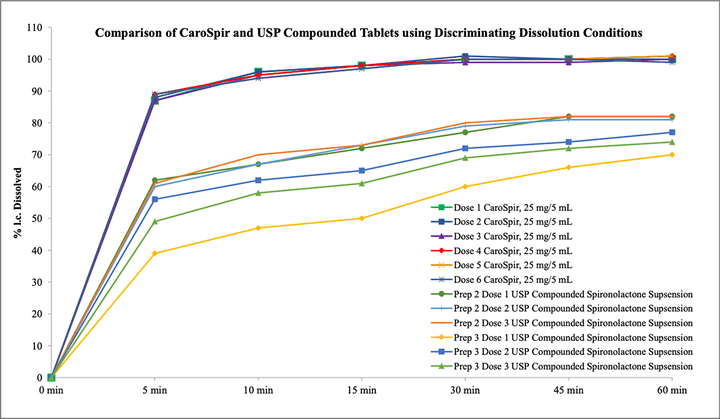
CAROSPIR oral suspension, 25 mg/5 mL, is not therapeutically equivalent to tablet forms of spironolactone. Follow dosing instructions for CAROSPIR. In patients requiring a dose greater than 100 mg, use another formulation of spironolactone. Doses of CAROSPIR suspension greater than 100 mg may result in spironolactone concentrations higher than expected.
Drug Interactions
- Agents increasing serum potassium: Concomitant administration can lead to hyperkalemia.
- Lithium: Increased risk of lithium toxicity.
- NSAIDs: May reduce the diuretic, natriuretic and antihypertensive effect of CAROSPIR.
- Digoxin: CAROSPIR can interfere with radioimmunologic assays of digoxin. Spironolactone and its metabolites increase the apparent exposure to digoxin.
- Cholestyramine: Hyperkalemic metabolic acidosis has been reported with concomitant use.
- Acetylsalicylic Acid (ASA): ASA may reduce the efficacy of spironolactone.
Please see Prescribing Information for additional safety information.